- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interleukin-17 cytokines: Effectors and targets in psoriasis—A breakthrough in understanding and treatment
Read this article at
Abstract
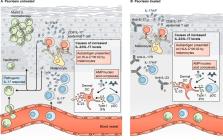
This review summarizes the steps from basic research on IL-17 family cytokines to understanding their role in psoriasis pathogenesis to the approval of a number of monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-17 pathways as first line treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Abstract
The IL-17 cytokine family comprising IL-17A to IL-17F and receptor subunits IL-17RA to IL-17RE represents a genetically ancient intercellular network regulating local tissue homeostasis. Its pivotal role in antifungal defense and its central position in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases including psoriasis were discovered only relatively late in the early 2000s. Since the connection of dysregulated IL-17 and psoriasis pathogenesis turned out to be particularly evident, a number of monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-17 pathways have been approved and are used as first line treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and further agents are currently in clinical development.
Related collections
Most cited references110
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found