- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Red Yeast Rice: A Systematic Review of the Traditional Uses, Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Quality Control of an Important Chinese Folk Medicine
Read this article at
Abstract
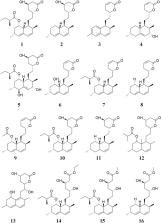
Red yeast rice (RYR), a Chinese traditional folk medicine produced by the fermentation of cooked rice kernels with a Monascaceae mold, Monascus purpureus, has long been used to treat blood circulation stasis, indigestion, diarrhea, and limb weakness in East Asian countries. This article provides a systematic review of the traditional uses, chemistry, biological activities, and toxicology of RYR to highlight its future prospects in the field of medicine. The literature reviewed for this article was obtained from the Web of Science, Elsevier, SciFinder, PubMed, CNKI, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, as well as Ph.D. and M.Sc. dissertations, published prior to July 2019. More than 101 chemical constituents have been isolated from RYR, mainly consisting of monacolins, pigments, organic acids, sterols, decalin derivatives, flavonoids, polysaccharides, and other compounds. Crude extracts of RYR, as well as its isolated compounds, possess broad pharmacological properties with hypolipidemic, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-cancer, neurocytoprotective, anti-osteoporotic, anti-fatigue, anti-diabetic, and anti-hypertensive activities. However, further studies are needed to characterize its diverse chemical constituents and the toxicological actions of the main bioactive compounds. New pharmacological trials addressing the overlooked traditional uses of RYR, such as in the treatment of indigestion and diarrhea, are required.
Related collections
Most cited references156
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Mycotoxins and their effects on human and animal health
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The worldwide diabetes epidemic.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found