- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
CRISPR-COPIES: an in silico platform for discovery of neutral integration sites for CRISPR/Cas-facilitated gene integration

Read this article at
Abstract
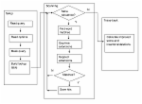
The CRISPR/Cas system has emerged as a powerful tool for genome editing in metabolic engineering and human gene therapy. However, locating the optimal site on the chromosome to integrate heterologous genes using the CRISPR/Cas system remains an open question. Selecting a suitable site for gene integration involves considering multiple complex criteria, including factors related to CRISPR/Cas-mediated integration, genetic stability, and gene expression. Consequently, identifying such sites on specific or different chromosomal locations typically requires extensive characterization efforts. To address these challenges, we have developed CRISPR-COPIES, a COmputational Pipeline for the Identification of CRISPR/Cas-facilitated int Egration Sites. This tool leverages ScaNN, a state-of-the-art model on the embedding-based nearest neighbor search for fast and accurate off-target search, and can identify genome-wide intergenic sites for most bacterial and fungal genomes within minutes. As a proof of concept, we utilized CRISPR-COPIES to characterize neutral integration sites in three diverse species: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Cupriavidus necator, and HEK293T cells. In addition, we developed a user-friendly web interface for CRISPR-COPIES ( https://biofoundry.web.illinois.edu/copies/). We anticipate that CRISPR-COPIES will serve as a valuable tool for targeted DNA integration and aid in the characterization of synthetic biology toolkits, enable rapid strain construction to produce valuable biochemicals, and support human gene and cell therapy applications.
Graphical Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references80
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
BLAST+: architecture and applications
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
MMseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive data sets
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
