- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The association between social isolation and musculoskeletal health in older community-dwelling adults: findings from the Hertfordshire Cohort Study
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
Social isolation has been associated with both physical and psychological adverse outcomes and is prevalent in older adults. We investigated the impact of social isolation on bone mineral density (BMD) and physical capability in community-dwelling older adults.
Methods
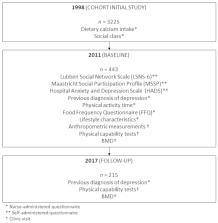
Data were collected in 2011 and 2017 from the Hertfordshire Cohort Study. In 2011, we assessed social isolation using the six-item Lubben Social Network Scale (LSNS-6) and the Maastricht Social Participation Profile (MSSP) and depressive and anxiety symptoms using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Physical capability was assessed by performing tests of gait speed, chair stands, timed up and go and balance at both time points. BMD was assessed using dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) at both time points.
Results
Data were available from 369 participants in 2011 and 184 in 2017. Forty percent of men and 42.4% of women were socially isolated. Isolated participants had higher odds of depressive disorder (OR 3.01, 95% CI 1.27–7.11, p < 0.02). Social isolation at baseline was associated with poor physical capability scores at follow-up (OR 5.53, 95% CI 1.09–27.99, p < 0.04). No associations were found between social isolation and BMD at either time point.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found