- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Age-period-cohort analysis of suicide mortality by gender among white and black Americans, 1983–2012
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Previous studies suggested that the racial differences in U.S. suicide rates are decreasing, particularly for African Americans, but the cause behind the temporal variations has yet to be determined. This study aims to investigate the long-term trends in suicide mortality in the U.S. between 1983 and 2012 and to examine age-, period-, and cohort-specific effects by gender and race.
Method
Suicide mortality data were collected from the Web-based Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System (WISQARS) and analyzed with the Joinpoint regression and age-period-cohort (APC) analysis.
Results
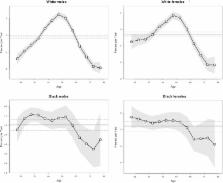
We found that although age-standardized rate of suicide in white males, white females, black males, and black females all changed at different degrees, the overall situation almost has not changed since these changes offset each other. By APC analysis, while the age effect on suicide demonstrate an obvious difference between white males and females (with the peak at 75 to 79 for white males and 45 to 54 for white females), young black people are predominantly susceptible to suicide (risk peaks in early 20s for black males and late 20s for black females). Cohort effects all showed a descending trend, except that in white males and females which showed an obvious increase peaked in around cohort 1960. There was a similar period effect trend between different genders in the same race group, but between the races, differences were found in the period before 1990 and after 2000.
Conclusion
We confirmed that the distinction in age-specific suicide rate patterns does exist by gender and by race after controlling for period and cohort effects, which suggested that minorities’ age patterns of suicide may have been masked up by the white people in the whole population. The differences of period effects and cohort effects between white and black Americans were likely to be mainly explained by the difference in race susceptibility to economic depression.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Suicide and suicidal behavior.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Estimating average annual per cent change in trend analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found