- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Reconstruction of the esophagojejunostomy by double stapling method using EEA™ OrVil™ in laparoscopic total gastrectomy and proximal gastrectomy
Read this article at
Abstract
Here we report the method of anastomosis based on double stapling technique (hereinafter, DST) using a trans-oral anvil delivery system (EEATM OrVilTM) for reconstructing the esophagus and lifted jejunum following laparoscopic total gastrectomy or proximal gastric resection.
As a basic technique, laparoscopic total gastrectomy employed Roux-en-Y reconstruction, laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy employed double tract reconstruction, and end-to-side anastomosis was used for the cut-off stump of the esophagus and lifted jejunum.
We used EEATM OrVilTM as a device that permitted mechanical purse-string suture similarly to conventional EEA, and endo-Surgitie.
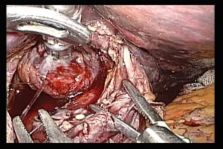
After the gastric lymph node dissection, the esophagus was cut off using an automated stapler. EEATM OrVilTM was orally and slowly inserted from the valve tip, and a small hole was created at the tip of the obliquely cut-off stump with scissors to let the valve tip pass through. Yarn was cut to disconnect the anvil from a tube and the anvil head was retained in the esophagus.
The end-Surgitie was inserted at the right subcostal margin, and after the looped-shaped thread was wrapped around the esophageal stump opening, assisting Maryland forceps inserted at the left subcostal and left abdomen were used to grasp the left and right esophageal stump. The surgeon inserted anvil grasping forceps into the right abdomen, and after grasping the esophagus with the forceps, tightened the end Surgitie, thereby completing the purse-string suture on the esophageal stump.
The main unit of the automated stapler was inserted from the cut-off stump of the lifted jejunum, and a trocar was made to pass through. To prevent dropout of the small intestines from the automated stapler, the automated stapler and the lifted jejunum were fastened with silk thread, the abdomen was again inflated, and the lifted jejunum was led into the abdominal cavity.
When it was confirmed that the automated stapler and center rod were made completely linear, the anvil and the main unit were connected with each other and firing was carried out. Then, DST-based anastomosis was completed with no dog-ear.
The method may facilitate safe laparoscopic anastomosis between the esophagus and reconstructed intestine. This is also considered to serve as a useful anastomosis technique for upper levels of the esophagus in laparotomy.
Related collections
Most cited references7
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intracorporeal circular stapling esophagojejunostomy using the transorally inserted anvil (OrVil) after laparoscopic total gastrectomy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Risk of peritonitis and fatal septicaemia and the need to defunction the low anastomosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found