- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Chinese Herbal Medicine on Dyslipidemia: Progress and Perspective
Read this article at
Abstract
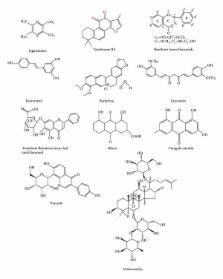
Dyslipidemia is an independent risk factor of cardiovascular diseases. The statins are a milestone in the primary and second prevention of cardiovascular diseases and significantly improved its prognosis. Along with the long-term treatment with statins in combination with other hypolipidemic drugs or alone, its safety has attracted a particular attention in clinic, such as the elevation of transaminase and rhabdomyolysis, which have raised an idea of developing the other types of lipid-lowering agents from botanic materials. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used in clinical practice for more than 2000 years in China and showed some beneficial effects for human health and many diseases. Recently, many studies demonstrated a favorable effect of TCM for treating dyslipidemia; however, its mechanism remains unclear or totally unknown. The progress and perspective of studies on dyslipidemia with single Chinese herb and its monomers or effective extracts during the past 10 years are discussed in the present review.
Related collections
Most cited references95
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Adults
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ginsenosides chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found