- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Advancing forensic-based investigation incorporating slime mould search for gene selection of high-dimensional genetic data
Read this article at
Abstract
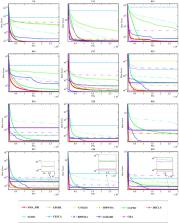
Modern medicine has produced large genetic datasets of high dimensions through advanced gene sequencing technology, and processing these data is of great significance for clinical decision-making. Gene selection (GS) is an important data preprocessing technique that aims to select a subset of feature information to improve performance and reduce data dimensionality. This study proposes an improved wrapper GS method based on forensic-based investigation (FBI). The method introduces the search mechanism of the slime mould algorithm in the FBI to improve the original FBI; the newly proposed algorithm is named SMA_FBI; then GS is performed by converting the continuous optimizer to a binary version of the optimizer through a transfer function. In order to verify the superiority of SMA_FBI, experiments are first executed on the 30-function test set of CEC2017 and compared with 10 original algorithms and 10 state-of-the-art algorithms. The experimental results show that SMA_FBI is better than other algorithms in terms of finding the optimal solution, convergence speed, and robustness. In addition, BSMA_FBI (binary version of SMA_FBI) is compared with 8 binary algorithms on 18 high-dimensional genetic data from the UCI repository. The results indicate that BSMA_FBI is able to obtain high classification accuracy with fewer features selected in GS applications. Therefore, SMA_FBI is considered an optimization tool with great potential for dealing with global optimization problems, and its binary version, BSMA_FBI, can be used for GS tasks.
Related collections
Most cited references74
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found