- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ecosystem state change in the Arabian Sea fuelled by the recent loss of snow over the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau region
Read this article at
Abstract
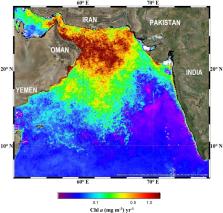
The recent trend of global warming has exerted a disproportionately strong influence on the Eurasian land surface, causing a steady decline in snow cover extent over the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau region. Here we show that this loss of snow is undermining winter convective mixing and causing stratification of the upper layer of the Arabian Sea at a much faster rate than predicted by global climate models. Over the past four decades, the Arabian Sea has also experienced a profound loss of inorganic nitrate. In all probability, this is due to increased denitrification caused by the expansion of the permanent oxygen minimum zone and consequent changes in nutrient stoichiometries. These exceptional changes appear to be creating a niche particularly favorable to the mixotroph, Noctiluca scintillans which has recently replaced diatoms as the dominant winter, bloom forming organism. Although Noctiluca blooms are non-toxic, they can cause fish mortality by exacerbating oxygen deficiency and ammonification of seawater. As a consequence, their continued range expansion represents a significant and growing threat for regional fisheries and the welfare of coastal populations dependent on the Arabian Sea for sustenance.
Related collections
Most cited references54
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found