- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Obesity and Multiple Sclerosis—A Multifaceted Association
Read this article at
Abstract
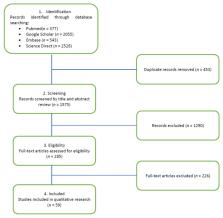
Background: Given the common elements in the pathophysiological theories that try to explain the appearance and evolution of obesity and multiple sclerosis, the association between the two pathologies has become an increasingly researched topic in recent years. On the one hand, there is the chronic demyelinating inflammation caused by the autoimmune cascade of multiple sclerosis, while on the other hand, according to the latest research, it has been shown that obesity shares an inflammatory component with most chronic diseases. Methods: The authors performed independent research of the available literature in the most important electronic databases (PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, and Science Direct) in February 2021. After applying the exclusion criteria, the reviewers focused on the most relevant articles published during the last 10 years with respect to epidemiology and pathophysiology. Results: The data presented are a step forward in trying to elucidate the intricate relationship between obesity and MS, especially the causal relationship between childhood and adolescent obesity and MS, focusing on the epidemiological associations observed in the most relevant observational studies conducted in recent years. In the second part, the authors comment on the latest findings related to the pathophysiological mechanisms that may explain the correlations between obesity and multiple sclerosis, focusing also on the role of adipokines. Conclusions: Based on available epidemiological data, obesity in early life appears to be strongly associated with a higher risk of MS development, independent of other risk factors. Although much research has been done on the pathophysiology of obesity, MS, their possible common mechanism, and the role of adipokines, further studies are needed in order to explain what remains unknown. No relevant data were found regarding the association between obesity, disability (high EDSS score), and mortality risk in MS patients. Thus, we consider that this topic should be elucidated in future research.
Related collections
Most cited references82
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota–gut–brain communication

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found