- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Host Immunological Factors Enhancing Mortality of Young Adults during the 1918 Influenza Pandemic

Read this article at
Abstract
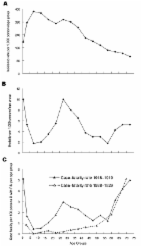
During the 1918 influenza pandemic, healthy young adults unusually succumbed to infection and were considered more vulnerable than young children and the elderly. The pathogenesis of this pandemic in the young adult population remains poorly understood. As this population is normally the least likely to die during seasonal influenza outbreaks, thought to be due to their appropriate pre-existing and robust immune responses protecting them from infection, we sought to review existing literature for immunological reasons for excessive mortality during the 1918 pandemic. We propose the novelty of the H1N1 pandemic virus to an H1N1 naïve immune system, the virulence of this virus, and dysfunctional host inflammatory and immunological responses, shaped by past influenza infections could have each contributed to their overall susceptibility. Additionally, in the young adult population, pre-exposure to past influenza infection of different subtypes, such as a H3N8 virus, during their infancy in 1889–1892, may have shaped immunological responses and enhanced vulnerability via humoral immunity effects with cross-reactive or non-neutralizing antibodies; excessive and/or ineffective cellular immunity from memory T lymphocytes; and innate dysfunctional inflammation. Multiple mechanisms likely contributed to the increased young adult mortality in 1918 and are the focus of this review.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cross-reactive antibody responses to the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found