- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Since the outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in December 2019, various digestive symptoms have been frequently reported in patients infected with the virus. In this study, we aimed to further investigate the prevalence and outcomes of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms.
METHODS:
In this descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study, we enrolled confirmed patients with COVID-19 who presented to 3 hospitals from January 18, 2020, to February 28, 2020. All patients were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction and were analyzed for clinical characteristics, laboratory data, and treatment. Data were followed up until March 18, 2020.
RESULTS:
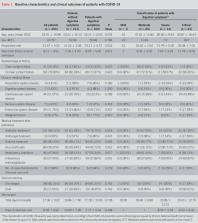
In the present study, 204 patients with COVID-19 and full laboratory, imaging, and historical data were analyzed. The average age was 52.9 years (SD ± 16), including 107 men and 97 women. Although most patients presented to the hospital with fever or respiratory symptoms, we found that 103 patients (50.5%) reported a digestive symptom, including lack of appetite (81 [78.6%] cases), diarrhea (35 [34%] cases), vomiting (4 [3.9%] cases), and abdominal pain (2 [1.9%] cases). If lack of appetite is excluded from the analysis (because it is less specific for the gastrointestinal tract), there were 38 total cases (18.6%) where patients presented with a gastrointestinal-specific symptom, including diarrhea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. Patients with digestive symptoms had a significantly longer time from onset to admission than patients without digestive symptoms (9.0 days vs 7.3 days). In 6 cases, there were digestive symptoms, but no respiratory symptoms. As the severity of the disease increased, digestive symptoms became more pronounced. Patients with digestive symptoms had higher mean liver enzyme levels, lower monocyte count, longer prothrombin time, and received more antimicrobial treatment than those without digestive symptoms.
DISCUSSION:
We found that digestive symptoms are common in patients with COVID-19. Moreover, these patients have a longer time from onset to admission, evidence of longer coagulation, and higher liver enzyme levels. Clinicians should recognize that digestive symptoms, such as diarrhea, are commonly among the presenting features of COVID-19 and that the index of suspicion may need to be raised earlier in at-risk patients presenting with digestive symptoms. However, further large sample studies are needed to confirm these findings.
Related collections
Most cited references18
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
