- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Do dentists practice what they know? A cross-sectional study on the agreement between dentists' knowledge and practice in restoring endodontically treated teeth

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
There are very few studies comparing dentists' knowledge in relation to their clinical approach despite the existence of a possible gap between what they know and what they do.
Aim
To measure the agreement between knowledge and practice methods related to a selected clinical scenario involving the placement of an indirect post in endodontically treated teeth (ETT) among different types of practitioners.
Methods
An electronic questionnaire was emailed to members of the Saudi Dental Society. The questionnaire presented a clinical scenario of restoring a posterior ETT with an indirect post, core unit, and crown, followed by specific questions regarding knowledge and practice related to ten different treatment aspects such as who prepares the post space, technique, isolation, time, gap between gutta-percha, and time to cementation of the crown. Each question was presented twice for each aspect, once asking about their practice method and then what they thought was the correct practice (knowledge). The relationship between the participants' responses and their specialty and the agreement between the responses of knowledge and practice for each participant were analyzed by Pearson's chi-square test and Kappa.
Results
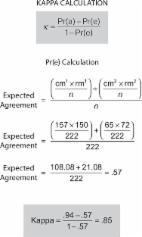
203 completed questionnaires were analyzed. Most participants were 30 years old or younger (62.6%), and general dental practitioners (59%). When comparing the knowledge to the practice methods of each participant, nine out of ten aspects were of a "weak" level agreement or below (kappa < 0.59, p < 0.001). Only one aspect demonstrated a "strong" level of agreement (Kappa = 0.804), which was related to the duration of time between obturation and post space preparation in the presence of a periapical lesion. However, this strong agreement in the responses was not aligned with current evidence. There was also a significant difference among the responses of endodontists, restorative dentists and general practitioners in most of the aspects.
Conclusion
Overall, there was a weak agreement between what practitioners know and do in most aspects of a selected clinical scenario involving the placement of an indirect post in posterior ETT. Moreover, the participant's specialty influenced their responses regarding both knowledge and clinical practice.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lost in knowledge translation: time for a map?
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found