- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Autocrine Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Activation Mediated by Integrin αVβ3 Regulates Transcriptional Expression of Laminin-332 in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney Epithelial Cells
Read this article at
Abstract
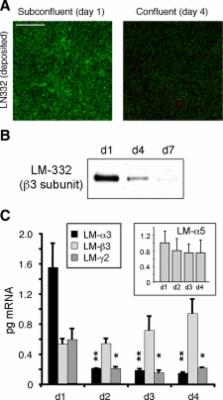
The expression of the extracellular matrix protein Laminin-332 is regulated transcriptionally by TGF-β1 as a function of cell confluence in MDCK epithelial cells. Latent TGF-β1 is secreted apically, sequestered from its receptors and activation machinery, dependent on integrin αVβ3, localized on the basolateral side of the epithelial barrier.
Abstract
Laminin (LM)-332 is an extracellular matrix protein that plays a structural role in normal tissues and is also important in facilitating recovery of epithelia from injury. We have shown that expression of LM-332 is up-regulated during renal epithelial regeneration after ischemic injury, but the molecular signals that control expression are unknown. Here, we demonstrate that in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells LM-332 expression occurs only in subconfluent cultures and is turned-off after a polarized epithelium has formed. Addition of active transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 to confluent MDCK monolayers is sufficient to induce transcription of the LM α3 gene and LM-332 protein expression via the TGF-β type I receptor (TβR-I) and the Smad2–Smad4 complex. Significantly, we show that expression of LM-332 in MDCK cells is an autocrine response to endogenous TGF-β1 secretion and activation mediated by integrin αVβ3 because neutralizing antibodies block LM-332 production in subconfluent cells. In confluent cells, latent TGF-β1 is secreted apically, whereas TβR-I and integrin αVβ3 are localized basolaterally. Disruption of the epithelial barrier by mechanical injury activates TGF-β1, leading to LM-332 expression. Together, our data suggest a novel mechanism for triggering the production of LM-332 after epithelial injury.
Related collections
Most cited references74
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
TGFbeta-SMAD signal transduction: molecular specificity and functional flexibility.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found