- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
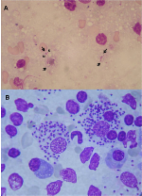
Treatment and follow-up of a domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo) with clinical leishmaniosis caused by Leishmania infantum
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
LeishVet guidelines for the practical management of canine leishmaniosis
Laia Solano-Gallego, Guadalupe Miró, Alek Koutinas … (2011)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Directions for the diagnosis, clinical staging, treatment and prevention of canine leishmaniosis.
L Solano-Gallego, A. Koutinas, G Miró … (2009)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Canine leishmaniosis - new concepts and insights on an expanding zoonosis: part one.
Gad Baneth, Alexander Koutinas, Laia Solano-Gallego … (2008)
