- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prenatal Household Air Pollution Exposure and Childhood Blood Pressure in Rural Ghana

Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
The association between prenatal household air pollution (HAP) exposure and childhood blood pressure (BP) is unknown.
Objective:
Within the Ghana Randomized Air Pollution and Health Study (GRAPHS) we examined time-varying associations between a) maternal prenatal and b) first-year-of-life HAP exposure with BP at 4 years of age and, separately, whether a stove intervention delivered prenatally and continued through the first year of life could improve BP at 4 years of age.
Methods:
GRAPHS was a cluster-randomized cookstove intervention trial wherein pregnant women were randomized to one of two stove interventions: a) a liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) stove or improved biomass stove, or b) control (open fire cooking). Maternal HAP exposure over pregnancy and child HAP exposure over the first year of life was quantified by repeated carbon monoxide (CO) measurements; a subset of women ( ) also performed one prenatal and one postnatal personal fine particulate matter ( ) measurement. Systolic and diastolic BP (SBP and DBP) were measured in 4-y-old children along with their exposure ( ). We examined the effect of the intervention on resting BP -scores. We also employed reverse distributed lag models to examine time-varying associations between a) maternal prenatal and b) first-year-of-life HAP exposure and resting BP -scores. Among those with measures, we examined associations between and resting BP -scores. Sex-specific effects were considered.
Results:
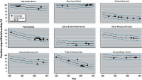
Intention-to-treat analyses identified that DBP -score at 4 years of age was lower among children born in the LPG arm (LPG ; 95% CI: , ) as compared with those in the control arm, and females were most susceptible to the intervention. Higher CO exposure in late gestation was associated with higher SBP and DBP -score at 4 years of age, whereas higher late-first-year-of-life CO exposure was associated with higher DBP -score. In the subset with measurements, higher maternal postnatal exposure was associated with higher SBP -scores.
Discussion:
These findings suggest that prenatal and first-year-of-life HAP exposure are associated with child BP and support the need for reductions in exposure to HAP, with interventions such as cleaner cooking beginning in pregnancy. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP13225
Related collections
Most cited references87

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Causal Diagrams for Epidemiologic Research
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
