- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Risk perceptions and preventive practices of COVID-19 among healthcare professionals in public hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Read this article at
Abstract
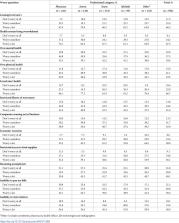
Healthcare professionals are at higher risk of contracting the new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although appropriate preventive measures are the most important interventions to prevent coronavirus infection among healthcare workers, they are also highly concerned about the consequences of the pandemic. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to assess preventive practices, perceived risk and worry about COVID-19 crisis among healthcare professionals at six public hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. A systematic random sampling technique was used to select 1,134 respondents (52.6% females). Data were collected between 9 th and 20 th June 2020 using self-administered questionnaires. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the data. A multiple linear regression analysis was performed to identify factors associated with worry about COVID-19 crisis. The highest percentage of respondents were nurses (39.3%) and physicians (22.2%), followed by interns (10.8%) and midwives (10.3%). Wearing facemask (93%) and frequent hand washing (93%) were the commonly reported preventive practices. Perceived risk of becoming infected with coronavirus (88%) and the potential risk of infection to their family (91%) were very high. The mean (median) worry score about COVID-19 crisis was 2.37 (3.0), on 1 to 3 scale, with 1 (not worried) and 3 (highly worried). The majority worried a lot about the health system being overwhelmed by COVID-19 patients (92%), the health of their loved ones (90%) and losing someone due to COVID-19 (89%). Respondents who had previously provided clinical care to Ebola, SARS and cholera patients had significantly lower levels of worry about COVID-19 crisis than participants who had not (β = -1.38, P<0.001). Our findings reveal respondents’ widespread practice of preventive measures, highest levels of perceived risk and worry about the COVID-19 crisis. Increased perceived risk and worry about COVID-19 might enable healthcare workers to adopt appropriate preventive measures more effectively against the disease.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The mental health of medical workers in Wuhan, China dealing with the 2019 novel coronavirus
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Understanding and Addressing Sources of Anxiety Among Health Care Professionals During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found