- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Innovative Randomized Phase I Study and Dosing Regimen Selection to Accelerate and Inform Pivotal COVID‐19 Trial of Nirmatrelvir

Read this article at
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) is a continued leading cause of hospitalization and death. Safe, efficacious COVID‐19 antivirals are needed urgently. Nirmatrelvir (PF‐07321332), the first orally bioavailable, severe acute respiratory syndrome‐coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) M pro inhibitor against the coronaviridae family, has demonstrated potent preclinical antiviral activity and benign safety profile. We report safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic data of nirmatrelvir with and without ritonavir as a pharmacokinetic enhancer, from an accelerated randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase I study. Two interleaving single‐ascending dose (SAD) cohorts were evaluated in a three‐period crossover. Multiple‐ascending dose (MAD) with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir twice daily (b.i.d.) dosing was evaluated over 10 days in five parallel cohorts. Safety was assessed, including in a supratherapeutic exposure cohort. Dose and dosing regimen for clinical efficacy evaluation in phase II/III clinical trials were supported by integrating modeling and simulations of SAD/MAD data with nonclinical data and a quantitative systems pharmacology model (QSP). In SAD, MAD, and supratherapeutic exposure cohorts, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was safe and well‐tolerated. Nirmatrelvir exposure and half‐life were considerably increased by ritonavir, enabling selection of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir dose and regimen for phase II/III trials (300/100 mg b.i.d.), to achieve concentrations continuously above those required for 90% inhibition of viral replication in vitro. The QSP model suggested that a 5‐day regimen would significantly decrease viral load in SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected patients which may prevent development of severe disease, hospitalization, and death. In conclusion, an innovative and seamless trial design expedited establishment of phase I safety and pharmacokinetics of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, enabling high confidence in phase II/III dose selection and accelerated pivotal trials’ initiation (NCT04756531).
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
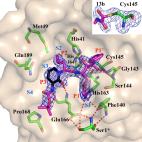
Structure of Mpro from COVID-19 virus and discovery of its inhibitors
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found