- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Telocytes in human epicardium
Read this article at
Abstract
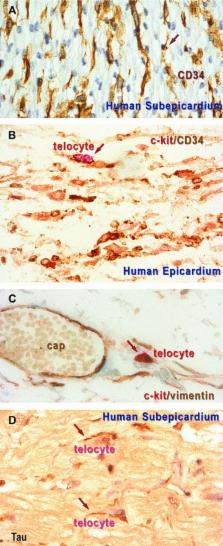
The existence of the epicardial telocytes was previously documented by immunohistochemistry (IHC) or immunofluorescence. We have also demonstrated recently that telocytes are present in mice epicardium, within the cardiac stem-cell niches, and, possibly, they are acting as nurse cells for the cardiomyocyte progenitors. The rationale of this study was to show that telocytes do exist in human (sub)epicardium, too. Human autopsy hearts from 10 adults and 15 foetuses were used for conventional IHC for c-kit/CD117, CD34, vimentin, S-100, τ, Neurokinin 1, as well as using laser confocal microscopy. Tissue samples obtained by surgical biopsies from 10 adults were studied by digital transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Double immunolabelling for c-kit/CD34 and, for c-kit/vimentin suggests that in human beings, epicardial telocytes share similar immunophenotype features with myocardial telocytes. The presence of the telocytes in human epicardium is shown by TEM. Epicardial telocytes, like any of the telocytes are defined by telopodes, their cell prolongations, which are very long (several tens of μm), very thin (0.1–0.2 μm, below the resolving power of light microscopy) and with moniliform configuration. The interconnected epicardial telocytes create a 3D cellular network, connected with the 3D network of myocardial telocytes. TEM documented that telocytes release shed microvesicles or exocytotic multivesicular bodies in the intercellular space. The human epicardial telocytes have similar phenotype (TEM and IHC) with telocytes located among human working cardiomyocyte. It remains to be established the role(s) of telocytes in cardiac renewing/repair/regeneration processes, and also the pathological aspects induced by their ‘functional inhibition’, or by their variation in number. We consider telocytes as a real candidate for future developments of autologous cell-based therapy in heart diseases.
Related collections
Most cited references62
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cardiac progenitor cells from adult myocardium: homing, differentiation, and fusion after infarction.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
