- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Multivariate logistic regression analysis on the association between anthropometric indicators of under-five children in Nigeria: NDHS 2018

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Child malnutrition is a huge health problem having multifaceted consequences for child survival and long-term well-being. Although, several studies investigated stunting, underweight, and wasting in low- and middle-income countries, in Nigeria, the link between them received little attention. The aim of this study is, therefore, to assess the association between anthropometric indicators of under-five children such as stunting, underweight and wasting given that of other characteristics of children and households.
Methods
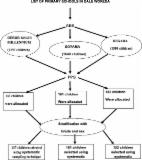
The data for this study was obtained from Nigerian Demographic and health survey (NDHS) in 2018. A total of 11,314 under-five children were involved. Multivariate logistic regression model was used to determine the association between stunting, underweight and wasting given that of the estimated effect of other determinants.
Results
From 11,314 under-five children the study considered 36.2, 21.4 and 6.7% of them suffered from stunting, underweight and wasting, respectively. About half (50.7%) of the children were male, 24.1% was obtained from North West region of Nigeria, and 37.8% of them were from households having unimproved drinking water. The pairwise dependency between stunting and underweight; underweight and wasting was measured using odds ratio (OR) of 15.796, and 16.750 respectively. The estimated odds of children from richest household to become stunted, underweight, and wasted was respectively 0.392, 0.540, 0.786 times that of the estimated odds of children from poorest households.
Conclusion
The prevalence of under-five children with stunting, underweight and/or wasting in Nigeria was very high. The important determinants of stunting, underweight, and wasting for under five children were household wealth index, women body mass index, sex of the child, anemia, mothers’ age at first birth, and a diarrhea two weeks prior to the survey. Whereas, region, religion, multiple birth, women’s educational level significantly associated with both stunting and underweight. Both stunting and wasting significantly associated with underweight.
Related collections
Most cited references18
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Wasting and stunting--similarities and differences: policy and programmatic implications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Determinants of stunting, underweight and wasting among children < 5 years of age: evidence from 2012-2013 Pakistan demographic and health survey
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found