- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Herbal Medicine for Cardiovascular Diseases: Efficacy, Mechanisms, and Safety
Read this article at
Abstract
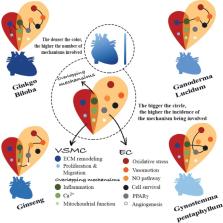
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a significant health burden with an ever-increasing prevalence. They remain the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The use of medicinal herbs continues to be an alternative treatment approach for several diseases including CVDs. Currently, there is an unprecedented drive for the use of herbal preparations in modern medicinal systems. This drive is powered by several aspects, prime among which are their cost-effective therapeutic promise compared to standard modern therapies and the general belief that they are safe. Nonetheless, the claimed safety of herbal preparations yet remains to be properly tested. Consequently, public awareness should be raised regarding medicinal herbs safety, toxicity, potentially life-threatening adverse effects, and possible herb–drug interactions. Over the years, laboratory data have shown that medicinal herbs may have therapeutic value in CVDs as they can interfere with several CVD risk factors. Accordingly, there have been many attempts to move studies on medicinal herbs from the bench to the bedside, in order to effectively employ herbs in CVD treatments. In this review, we introduce CVDs and their risk factors. Then we overview the use of herbs for disease treatment in general and CVDs in particular. Further, data on the ethnopharmacological therapeutic potentials and medicinal properties against CVDs of four widely used plants, namely Ginseng, Ginkgo biloba, Ganoderma lucidum, and Gynostemma pentaphyllum, are gathered and reviewed. In particular, the employment of these four plants in the context of CVDs, such as myocardial infarction, hypertension, peripheral vascular diseases, coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathies, and dyslipidemias has been reviewed, analyzed, and critically discussed. We also endeavor to document the recent studies aimed to dissect the cellular and molecular cardio-protective mechanisms of the four plants, using recently reported in vitro and in vivo studies. Finally, we reviewed and reported the results of the recent clinical trials that have been conducted using these four medicinal herbs with special emphasis on their efficacy, safety, and toxicity.
Related collections
Most cited references284
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cytokines in atherosclerosis: pathogenic and regulatory pathways.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found