- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Data Gathering Bias: Trait Vulnerability to Psychotic Symptoms?
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Jumping to conclusions (JTC) is associated with psychotic disorder and psychotic symptoms. If JTC represents a trait, the rate should be (i) increased in people with elevated levels of psychosis proneness such as individuals diagnosed with borderline personality disorder (BPD), and (ii) show a degree of stability over time.
Methods
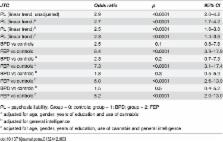
The JTC rate was examined in 3 groups: patients with first episode psychosis (FEP), BPD patients and controls, using the Beads Task. PANSS, SIS-R and CAPE scales were used to assess positive psychotic symptoms. Four WAIS III subtests were used to assess IQ.
Results
A total of 61 FEP, 26 BPD and 150 controls were evaluated. 29 FEP were revaluated after one year. 44% of FEP (OR = 8.4, 95% CI: 3.9–17.9) displayed a JTC reasoning bias versus 19% of BPD (OR = 2.5, 95% CI: 0.8–7.8) and 9% of controls. JTC was not associated with level of psychotic symptoms or specifically delusionality across the different groups. Differences between FEP and controls were independent of sex, educational level, cannabis use and IQ. After one year, 47.8% of FEP with JTC at baseline again displayed JTC.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Psychosis as a state of aberrant salience: a framework linking biology, phenomenology, and pharmacology in schizophrenia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Short form of the WAIS-III for use with patients with schizophrenia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found