- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Electric control of spin transitions at the atomic scale
Read this article at
Abstract
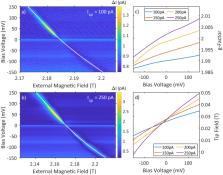
Electric control of spins has been a longstanding goal in the field of solid state physics due to the potential for increased efficiency in information processing. This efficiency can be optimized by transferring spintronics to the atomic scale. We present electric control of spin resonance transitions in single TiH molecules by employing electron spin resonance scanning tunneling microscopy (ESR-STM). We find strong bias voltage dependent shifts in the ESR signal of about ten times its line width. We attribute this to the electric field in the tunnel junction, which induces a displacement of the spin system changing the g-factor and the effective magnetic field of the tip. We demonstrate direct electric control of the spin transitions in coupled TiH dimers. Our findings open up new avenues for fast coherent control of coupled spin systems and expands on the understanding of spin electric coupling.
Abstract
Control of spins down to the atomic scale is a major goal for spin-based information processing. Here, Kot et al. demonstrate electric control over the spin-resonance transitions of a single TiH molecule placed on a surface of MgO by exploiting the electric field between the scanning tunnelling microscopy tip and the sample.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Electronic analog of the electro-optic modulator
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Spin Hall effects
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found