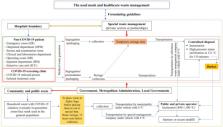
To the Editor: A novel human coronavirus that is now named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (formerly called HCoV-19) emerged in Wuhan, China, in late 2019 and is now causing a pandemic. 1 We analyzed the aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 and compared it with SARS-CoV-1, the most closely related human coronavirus. 2 We evaluated the stability of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 in aerosols and on various surfaces and estimated their decay rates using a Bayesian regression model (see the Methods section in the Supplementary Appendix, available with the full text of this letter at NEJM.org). SARS-CoV-2 nCoV-WA1-2020 (MN985325.1) and SARS-CoV-1 Tor2 (AY274119.3) were the strains used. Aerosols (<5 μm) containing SARS-CoV-2 (105.25 50% tissue-culture infectious dose [TCID50] per milliliter) or SARS-CoV-1 (106.75-7.00 TCID50 per milliliter) were generated with the use of a three-jet Collison nebulizer and fed into a Goldberg drum to create an aerosolized environment. The inoculum resulted in cycle-threshold values between 20 and 22, similar to those observed in samples obtained from the upper and lower respiratory tract in humans. Our data consisted of 10 experimental conditions involving two viruses (SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1) in five environmental conditions (aerosols, plastic, stainless steel, copper, and cardboard). All experimental measurements are reported as means across three replicates. SARS-CoV-2 remained viable in aerosols throughout the duration of our experiment (3 hours), with a reduction in infectious titer from 103.5 to 102.7 TCID50 per liter of air. This reduction was similar to that observed with SARS-CoV-1, from 104.3 to 103.5 TCID50 per milliliter (Figure 1A). SARS-CoV-2 was more stable on plastic and stainless steel than on copper and cardboard, and viable virus was detected up to 72 hours after application to these surfaces (Figure 1A), although the virus titer was greatly reduced (from 103.7 to 100.6 TCID50 per milliliter of medium after 72 hours on plastic and from 103.7 to 100.6 TCID50 per milliliter after 48 hours on stainless steel). The stability kinetics of SARS-CoV-1 were similar (from 103.4 to 100.7 TCID50 per milliliter after 72 hours on plastic and from 103.6 to 100.6 TCID50 per milliliter after 48 hours on stainless steel). On copper, no viable SARS-CoV-2 was measured after 4 hours and no viable SARS-CoV-1 was measured after 8 hours. On cardboard, no viable SARS-CoV-2 was measured after 24 hours and no viable SARS-CoV-1 was measured after 8 hours (Figure 1A). Both viruses had an exponential decay in virus titer across all experimental conditions, as indicated by a linear decrease in the log10TCID50 per liter of air or milliliter of medium over time (Figure 1B). The half-lives of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 were similar in aerosols, with median estimates of approximately 1.1 to 1.2 hours and 95% credible intervals of 0.64 to 2.64 for SARS-CoV-2 and 0.78 to 2.43 for SARS-CoV-1 (Figure 1C, and Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix). The half-lives of the two viruses were also similar on copper. On cardboard, the half-life of SARS-CoV-2 was longer than that of SARS-CoV-1. The longest viability of both viruses was on stainless steel and plastic; the estimated median half-life of SARS-CoV-2 was approximately 5.6 hours on stainless steel and 6.8 hours on plastic (Figure 1C). Estimated differences in the half-lives of the two viruses were small except for those on cardboard (Figure 1C). Individual replicate data were noticeably “noisier” (i.e., there was more variation in the experiment, resulting in a larger standard error) for cardboard than for other surfaces (Fig. S1 through S5), so we advise caution in interpreting this result. We found that the stability of SARS-CoV-2 was similar to that of SARS-CoV-1 under the experimental circumstances tested. This indicates that differences in the epidemiologic characteristics of these viruses probably arise from other factors, including high viral loads in the upper respiratory tract and the potential for persons infected with SARS-CoV-2 to shed and transmit the virus while asymptomatic. 3,4 Our results indicate that aerosol and fomite transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is plausible, since the virus can remain viable and infectious in aerosols for hours and on surfaces up to days (depending on the inoculum shed). These findings echo those with SARS-CoV-1, in which these forms of transmission were associated with nosocomial spread and super-spreading events, 5 and they provide information for pandemic mitigation efforts.