- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MicroRNA-223 Suppresses the Canonical NF-κB Pathway in Basal Keratinocytes to Dampen Neutrophilic Inflammation

Read this article at
SUMMARY
MicroRNA-223 is known as a myeloid-enriched anti-inflammatory microRNA that is dysregulated in numerous inflammatory conditions. Here, we report that neutrophilic inflammation (wound response) is augmented in miR-223-deficient zebrafish, due primarily to elevated activation of the canonical nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway. NF-κB over-activation is restricted to the basal layer of the surface epithelium, although miR-223 is detected throughout the epithelium and in phagocytes. Not only phagocytes but also epithelial cells are involved in miR-223-mediated regulation of neutrophils’ wound response and NF-κB activation. Cul1a/b, Traf6, and Tab1 are identified as direct targets of miR-223, and their levels rise in injured epithelium lacking miR-223. In addition, miR-223 is expressed in cultured human bronchial epithelial cells, where it also downregulates NF-κB signaling. Together, this direct connection between miR-223 and the canonical NF-κB pathway provides a mechanistic understanding of the multifaceted role of miR-223 and highlights the relevance of epithelial cells in dampening neutrophil activation.
In Brief
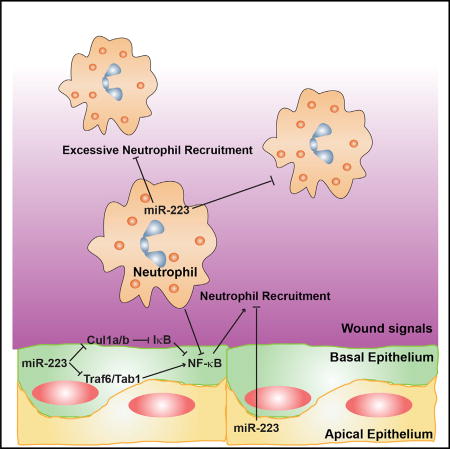
microRNA-223 is dysregulated in many inflammatory conditions such as cancer and asthma, yet its physiological role is not clear. Zhou et al. demonstrate that microRNA-223 in both phagocytes and epithelial cells cooperate to suppress the canonical NF-κB pathway in epithelial cells to restrict the magnitude of inflammation.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A tissue-scale gradient of hydrogen peroxide mediates rapid wound detection in zebrafish
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Regulation of progenitor cell proliferation and granulocyte function by microRNA-223.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found