- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Multimodality imaging in lobular breast cancer: Differences in mammography, ultrasound, and MRI in the assessment of local tumor extent and correlation with molecular characteristics
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Invasive lobular breast cancer (ILC) is a diagnostic challenge due to the diversity of morphological features. The objective of the study was to investigate the presentation and local extent of ILC using various imaging techniques and to assess the correlation between imaging and molecular profile.
Materials and methods
We reviewed 162 consecutive patients with ILC found on vacuum-assisted biopsy, who underwent evaluation of the lesion morphology and extent using ultrasound (US), mammography (MMG), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Radiographic features were compared with ILC intrinsic subtype based on the expression of Ki-67 and estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors.
Results
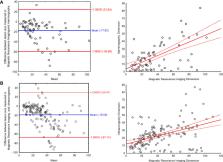
A total of 113 mass lesions and 49 non-mass enhancements (NMEs) were found in MRI. Masses were typically irregular and spiculated, showing heterogeneous contrast enhancement, diffusion restriction, and type III enhancement curve. NMEs presented mainly as the area of focal or multiregional distribution with heterogeneous or clumped contrast enhancement, diffusion restriction, and type III enhancement curve. Lesion extent significantly varied between MRI and MMG/ultrasonography (USG) (P < 0.001) but did not differ between MGF and ultrasonography (USG). The larger the ILC, the higher the disproportion when lesion extent in MRI was compared with MMG (P < 0.001) and ultrasonography (USG) (P < 0.001). In the study group, there were 97 cases of luminal A subtype (59.9%), 54 cases of luminal B HER2− (33.3%), nine cases of luminal B HER2+ (5.5%), and two cases of triple negative (1.2%). The HER2 type was not found in the study group. We did not observe any significant correlation between molecular profile and imaging.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The HER-2 receptor and breast cancer: ten years of targeted anti-HER-2 therapy and personalized medicine.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Diagnostic accuracy of mammography, clinical examination, US, and MR imaging in preoperative assessment of breast cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found