- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Baleen boom and bust: a synthesis of mysticete phylogeny, diversity and disparity
Read this article at
Abstract
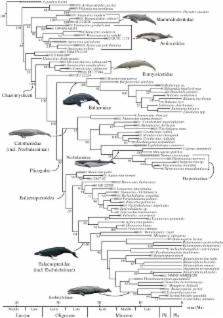
A new, fully dated total-evidence phylogeny of baleen whales (Mysticeti) shows that evolutionary phases correlate strongly with Caenozoic modernization of the oceans and climates, implying a major role for bottom-up physical drivers. The phylogeny of 90 modern and dated fossil species suggests three major phases in baleen whale history: an early adaptive radiation (36–30 Ma), a shift towards bulk filter-feeding (30–23 Ma) and a climate-driven diversity loss around 3 Ma. Evolutionary rates and disparity were high following the origin of mysticetes around 38 Ma, coincident with global cooling, abrupt Southern Ocean eutrophication and the development of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC). Subsequently, evolutionary rates and disparity fell, becoming nearly constant after approximately 23 Ma as the ACC reached its full strength. By contrast, species diversity rose until 15 Ma and then remained stable, before dropping sharply with the onset of Northern Hemisphere glaciation. This decline coincided with the final establishment of modern mysticete gigantism and may be linked to glacially driven variability in the distribution of shallow habitats or an increased need for long-distance migration related to iron-mediated changes in glacial marine productivity.
Related collections
Most cited references60
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
AWTY (are we there yet?): a system for graphical exploration of MCMC convergence in Bayesian phylogenetics.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found