- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Association between plasma fibrinogen and survival in patients with small‐cell lung carcinoma
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
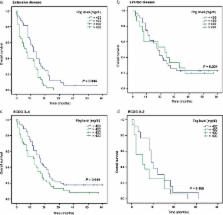
Elevated plasma fibrinogen (Fbg) levels contribute to tumor progression and metastasis; however, limited research on Fbg in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has been conducted. This study evaluated the prognostic value of Fbg levels in patients with SCLC.
Methods
Data on plasma Fbg level, clinical features, and overall survival were retrospectively collected. Kaplan–Meier estimates and log‐rank tests were used to analyze the relationship between Fbg level and survival. Multivariate analyses were performed to determine independent prognostic factors. Subgroup analyses were performed based on extensive/limited disease and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group status.
Results
A total of 120 patients with SCLC were included. The one, three, and five‐year survival rates for the entire cohort were 48.3%, 9.2%, and 1.7%, respectively. Univariate analyses revealed that age, alcohol use, clinical stage, pleural effusion, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group grade, and Fbg and lactate dehydrogenase levels were associated with survival ( P < 0.05). The median survival time for patients with high Fbg levels (> 400 mg/dL) was shorter than for those with low Fbg levels (8 vs. 14 months; P = 0.013). Furthermore, multivariate analysis revealed that Fbg was negatively and independently associated with SCLC prognosis (hazard ratio 1.505, 95% confidence interval 1.018–2.226; P = 0.041). Higher Fbg levels were associated with shorter survival in the extensive disease subgroup (7 vs. 12 months; P = 0.004).
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
High D-dimer levels are associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Vascular endothelial growth factor binds to fibrinogen and fibrin and stimulates endothelial cell proliferation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found