- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Early diving behaviour in juvenile penguins: improvement or selection processes
Read this article at
Abstract
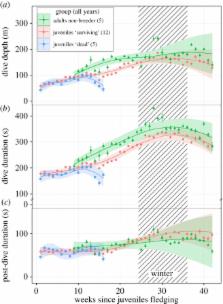
The early life stage of long-lived species is critical to the viability of population, but is poorly understood. Longitudinal studies are needed to test whether juveniles are less efficient foragers than adults as has been hypothesized. We measured changes in the diving behaviour of 17 one-year-old king penguins Aptenodytes patagonicus at Crozet Islands (subantartic archipelago) during their first months at sea, using miniaturized tags that transmitted diving activity in real time. We also equipped five non-breeder adults with the same tags for comparison. The data on foraging performance revealed two groups of juveniles. The first group made shallower and shorter dives that may be indicative of early mortality while the second group progressively increased their diving depths and durations, and survived the first months at sea. This surviving group of juveniles required the same recovery durations as adults, but typically performed shallower and shorter dives. There is thereby a relationship between improved diving behaviour and survival in young penguins. This long period of improving diving performance in the juvenile life stage is potentially a critical period for the survival of deep avian divers and may have implications for their ability to adapt to environmental change.
Related collections
Most cited references6
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
How life history influences population dynamics in fluctuating environments.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
From cradle to early grave: juvenile mortality in European shags Phalacrocorax aristotelis results from inadequate development of foraging proficiency.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found