- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
COVID-19 is rapidly changing: Examining public perceptions and behaviors in response to this evolving pandemic
Abstract
Background
Since the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in late 2019, communities have been required to rapidly adopt community mitigation strategies rarely used before, or only in limited settings. This study aimed to examine the attitudes and beliefs of Australian adults towards the COVID-19 pandemic, and willingness and capacity to engage with these mitigation measures. In addition, we aimed to explore the psychosocial and demographic factors that are associated with adoption of recommended hygiene-related and avoidance-related behaviors.
Methods
A national cross-sectional online survey of 1420 Australian adults (18 years and older) was undertaken between the 18 and 24 March 2020. The statistical analysis of the data included univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Findings
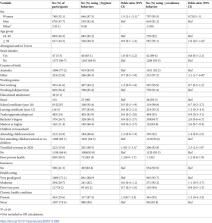
The survey of 1420 respondents found 50% (710) of respondents felt COVID-19 would ‘somewhat’ affect their health if infected and 19% perceived their level of risk as high or very high. 84·9% had performed ≥1 of the three recommended hygiene-related behaviors and 93·4% performed ≥1 of six avoidance-related behaviors over the last one month. Adopting avoidance behaviors was associated with trust in government/authorities (aOR: 6.0, 95% CI 2.6–11·0), higher perceived rating of effectiveness of behaviors (aOR: 4·0, 95% CI: 1·8–8·7), higher levels of perceived ability to adopt social distancing strategies (aOR: 5.0, 95% CI: 1·5–9.3), higher trust in government (aOR: 6.0, 95% CI: 2.6–11.0) and higher level of concern if self-isolated (aOR: 1.8, 95% CI: 1.1–3.0).
Interpretation
In the last two months, members of the public have been inundated with messages about hygiene and social (physical) distancing. However, our results indicate that a continued focus on supporting community understanding of the rationale for these strategies, as well as instilling community confidence in their ability to adopt or sustain the recommendations is needed.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Public knowledge, attitudes and practices towards COVID-19: A cross-sectional study in Malaysia

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found