- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical effectiveness of manual therapy for the management of musculoskeletal and non-musculoskeletal conditions: systematic review and update of UK evidence report
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
This systematic review updated and extended the "UK evidence report" by Bronfort et al. (Chiropr Osteopath 18:3, 2010) with respect to conditions/interventions that received an 'inconclusive’ or 'negative’ evidence rating or were not covered in the report.
Methods
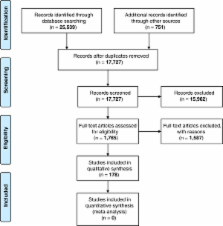
A literature search of more than 10 general medical and specialised databases was conducted in August 2011 and updated in March 2013. Systematic reviews, primary comparative studies and qualitative studies of patients with musculoskeletal or non-musculoskeletal conditions treated with manual therapy and reporting clinical outcomes were included. Study quality was assessed using standardised instruments, studies were summarised, and the results were compared against the evidence ratings of Bronfort. These were either confirmed, updated, or new categories not assessed by Bronfort were added.
Results
25,539 records were found; 178 new and additional studies were identified, of which 72 were systematic reviews, 96 were randomised controlled trials, and 10 were non-randomised primary studies. Most 'inconclusive’ or 'moderate’ evidence ratings of the UK evidence report were confirmed. Evidence ratings changed in a positive direction from inconclusive to moderate evidence ratings in only three cases (manipulation/mobilisation [with exercise] for rotator cuff disorder; spinal mobilisation for cervicogenic headache; and mobilisation for miscellaneous headache). In addition, evidence was identified on a large number of non-musculoskeletal conditions not previously considered; most of this evidence was rated as inconclusive.
Related collections
Most cited references181
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
External Validation of a Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A comparison of physical therapy, chiropractic manipulation, and provision of an educational booklet for the treatment of patients with low back pain.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found