- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Natural disasters and infectious disease in Europe: a literature review to identify cascading risk pathways
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Natural disasters are increasing in their frequency and complexity. Understanding how their cascading effects can lead to infectious disease outbreaks is important for developing cross-sectoral preparedness strategies. The review focussed on earthquakes and floods because of their importance in Europe and their potential to elucidate the pathways through which natural disasters can lead to infectious disease outbreaks.
Methods
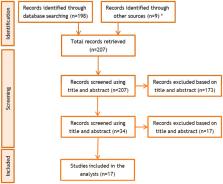
A systematic literature review complemented by a call for evidence was conducted to identify earthquake or flooding events in Europe associated with potential infectious disease events.
Results
This review included 17 peer-reviewed papers that reported on suspected and confirmed infectious disease outbreaks following earthquakes (4 reports) or flooding (13 reports) in Europe. The majority of reports related to food- and water-borne disease. Eleven studies described the cascading effect of post-disaster outbreaks. The most reported driver of disease outbreaks was heavy rainfall, which led to cross-connections between water and other environmental systems, leading to the contamination of rivers, lakes, springs and water supplies. Exposure to contaminated surface water or floodwater following flooding, exposure to animal excreta and post-disaster living conditions were among other reported drivers of outbreaks.
Conclusions
The cascade effects of natural disasters, such as earthquakes and floods, include outbreaks of infectious disease. The projection that climate change-related extreme weather events will increase in Europe in the coming century highlights the importance of strengthening preparedness planning and measures to mitigate and control outbreaks in post-disaster settings.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Increasing risk over time of weather-related hazards to the European population: a data-driven prognostic study
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Public health. Monitoring EU emerging infectious disease risk due to climate change.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found