- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Global Financial Crisis, Smart Lockdown Strategies, and the COVID-19 Spillover Impacts: A Global Perspective Implications From Southeast Asia
Read this article at
Abstract
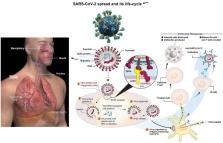
This present study primarily emphasizes to seek the COVID-19 adverse impacts posing health challenges and global economic crisis. The pandemic (COVID-19) continues to hit the global economies adversely. Pakistan is the 5th-most-populous nation, and recorded positive cases with the third-highest positivity ratio in South Asia, and 26th-highest deaths toll of 21,450 and 29th number of most COVID-19 positive cases with 933,750 worldwide, as of June 6, 2021. The first wave appeared at the end of May 2020, and mid of June reported its peak, which ended by mid-July 2020. Early November 2020 witnessed the second wave with low intensity reached the climax by mid-December. The COVID-19's third wave severely affected the country during mid-March 2021. It exhibited the highest positivity rate, around 20%. New positive patients and deaths toll commenced to skyrocket and reported peak by April 15, 2021. Then situation gradually improved with effective measures and restrictions. The pandemic coronavirus (COVID-19) has affected 220 territories, regions, and countries and resulted in more than 174.116 million infections, deaths, 3.75 million, and 157.157 million positive cases fully recovered from this infectious disease, as of June 7, 2021. The pandemic has caused a severe crisis of healthcare facilities and economic challenges worldwide. Pakistani economy reported GPD's negative growth (–0.05) for the first time over the last 60 years in 2020, which caused a massive financial crisis. The Government's relief package intervened to reduce public mental stress and improve the quality of their lives. IMF reported that Pakistan's GPD bounced back at 4% growth by June 2021. This article determines that economic instability and health burden happened in Pakistan for a longer time than financial disequilibrium that occurred globally. Pakistan encountered this crisis due to its feeble healthcare systems and fragile economy. This study explores adverse health issues and spillover consequences on the economic crisis in Pakistan with global implications. It recommends smart lockdown restrictions in most affected areas to reopen the economic cycle with strict preventive measures to minimize the COVD-19 adverse consequences.
Related collections
Most cited references107

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Occurrence and transmission potential of asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections: A living systematic review and meta-analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Tourism and COVID-19: impacts and implications for advancing and resetting industry and research
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found