- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Flexo-Ionic Effect of Ionic Liquid Crystal Elastomers
Read this article at
Abstract
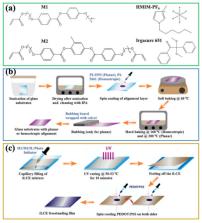
The first study of the flexo-ionic effect, i.e., mechanical deformation-induced electric signal, of the recently discovered ionic liquid crystal elastomers (iLCEs) is reported. The measured flexo-ionic coefficients were found to strongly depend on the director alignment of the iLCE films and can be over 200 µC/m. This value is orders of magnitude higher than the flexo-electric coefficient found in insulating liquid crystals and is comparable to the well-developed ionic polymers (iEAPs). The shortest response times, i.e., the largest bandwidth of the flexo-ionic responses, is achieved in planar alignment, when the director is uniformly parallel to the substrates. These results render high potential for iLCE-based devices for applications in sensors and wearable micropower generators.
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Piezoelectric Effects in Liquid Crystals
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Collective diffusion, nucleation, and spinodal decomposition in polymer mixtures
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found