- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Awareness, attitudes, and practices related to the swine influenza pandemic among the Saudi public
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
During an infectious disease outbreak, it is critical to learn as much as possible about the concerns, knowledge, attitudes, and behavior of the public. Such information can be crucial to the improvement of communication efforts by public health officials and clinicians. The aim of this study was to identify awareness, attitudes, and practices related to influenza A (H1N1) among the Saudi public.
Methods
A cross-sectional study of 1,548 adult subjects recruited from various shopping malls in Riyadh and Jeddah was conducted. All of the subjects were interviewed using a questionnaire that tested their knowledge, attitudes, and use of precautionary measures in relation to the H1N1 influenza pandemic.
Results
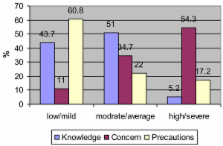
More than half (54.3%, 840/1548) of the participants showed high concern, 43.7%(677/1548) showed a low level of knowledge, and 60.8%(941/1548) had taken minimal or no precautionary measures. After adjusting for other variables, education level was the only significant predictor of the level of concern (p < 0.001), while greater precautionary measures were taken by participants who were male (p < 0.001), older (p = 0.047), better educated (p = 0.04), and more knowledgeable (p < 0.001). More than one-third (38.3%) of participants were not convinced that the MOH reports about the disease were true, and only 16.1% of the participants reported receiving information from health providers.
Conclusions
High concern did not translate into a higher compliance with precautionary recommendations, possibly due to the low level of knowledge about the disease among the public. Frequent communication between physicians and the public is recommended to help dispel myths about the disease and to spread better information about the role that the public can play in limiting the spread of the disease.
Related collections
Most cited references9

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Non-pharmaceutical public health interventions for pandemic influenza: an evaluation of the evidence base
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Factors influencing the wearing of facemasks to prevent the severe acute respiratory syndrome among adult Chinese in Hong Kong
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found