- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Social Stratification, Diet Diversity and Malnutrition among Preschoolers: A Survey of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia

Read this article at
Abstract
In Sub-Saharan Africa, being overweight in childhood is rapidly rising while stunting is still remaining at unacceptable levels. A key contributor to this double burden of malnutrition is dietary changes associated with nutrition transition. Although the importance of socio-economic drivers is known, there is limited knowledge about their stratification and relative importance to diet and to different forms of malnutrition. The aim of this study was to assess diet diversity and malnutrition in preschoolers and evaluate the relative importance of socioeconomic resources. Households with children under five (5467) were enrolled using a multi-stage sampling procedure. Standardized tools and procedures were used to collect data on diet, anthropometry and socio-economic factors. Multivariable analysis with cluster adjustment was performed. The prevalence of stunting was 19.6% (18.5–20.6), wasting 3.2% (2.8–3.7), and overweight/obesity 11.4% (10.6–12.2). Stunting, overweight, wasting and limited diet diversity was present in all social strata. Low maternal education was associated with an increased risk of stunting (Adjusted odds ratio (AOR): 1.8; 1.4–2.2), limited diet diversity (AOR: 0.33; 0.26–0.42) and reduced odds of being overweight (AOR: 0.61; 0.44–0.84). Preschoolers in Addis Ababa have limited quality diets and suffer from both under- and over-nutrition. Maternal education was an important explanatory factor for stunting and being overweight. Interventions that promote diet quality for the undernourished whilst also addressing the burgeoning problem of being overweight are needed.
Related collections
Most cited references43
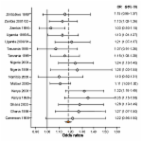
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Boys are more stunted than girls in Sub-Saharan Africa: a meta-analysis of 16 demographic and health surveys
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Uneven dietary development: linking the policies and processes of globalization with the nutrition transition, obesity and diet-related chronic diseases
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found