- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
USP15 Deubiquitinase Safeguards Hematopoiesis and Genome Integrity in Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Leukemia Cells

Read this article at
Summary
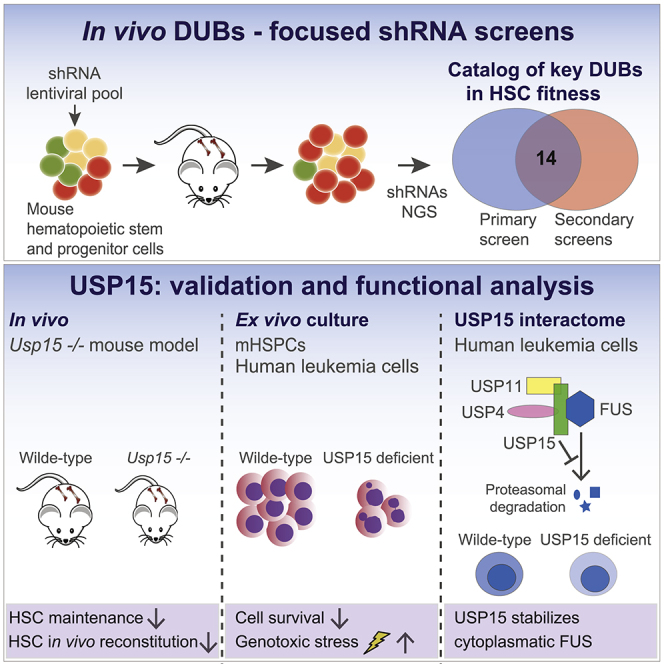
Altering ubiquitination by disruption of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) affects hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) maintenance. However, comprehensive knowledge of DUB function during hematopoiesis in vivo is lacking. Here, we systematically inactivate DUBs in mouse hematopoietic progenitors using in vivo small hairpin RNA (shRNA) screens. We find that multiple DUBs may be individually required for hematopoiesis and identify ubiquitin-specific protease 15 (USP15) as essential for HSC maintenance in vitro and in transplantations and Usp15 knockout (KO) mice in vivo. USP15 is highly expressed in human hematopoietic tissues and leukemias. USP15 depletion in murine progenitors and leukemia cells impairs in vitro expansion and increases genotoxic stress. In leukemia cells, USP15 interacts with and stabilizes FUS (fused in sarcoma), a known DNA repair factor, directly linking USP15 to the DNA damage response (DDR). Our study underscores the importance of DUBs in preserving normal hematopoiesis and uncovers USP15 as a critical DUB in safeguarding genome integrity in HSCs and leukemia cells.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
-
•
In vivo shRNAs screens for deubiquitinases identify regulators of murine hematopoiesis
-
•
Usp15 deletion compromises HSC maintenance and reconstitution potential in vivo
-
•
USP15 loss affects genome integrity and growth of mHSPCs and human leukemia cells
-
•
In human leukemia cells, USP15 stabilizes its interactor, FUS, a DNA repair factor
Abstract
Van den Berk et al. use unbiased in vivo RNAi screens targeting deubiquitinases in mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. This study underscores the importance of deubiquitinases in hematopoietic stem cell function and reveals the role of USP15 in preserving genome integrity in normal and transformed hematopoietic cells.
Related collections
Most cited references92
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found