- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Open Campus Policies: How Built, Food, Social, and Organizational Environments Matter for Oregon’s Public High School Students’ Health

Read this article at
Abstract
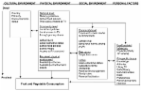
Open campus policies that grant access to the off-campus food environment may influence U.S. high school students’ exposure to unhealthy foods, yet predictors of these policies are unknown. Policy holding and built (walkability), food (access to grocery stores), social (school-to-neighborhood demographic similarity), and organizational (policy holding of neighboring schools) environment data were collected for 200 Oregon public high schools. These existing data were derived from the Oregon School Board Association, WalkScore.com, the 2010 Decennial Census, the 2010–2014 American Community Survey, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, TDLinex, Nielson directories, the U.S. Department of Education, the National Center for Education Statistics, and the Common Core of Data. Most (67%) of Oregon public high schools have open campus policies. Logistic regression analyses modeled open campus policy holding as a function of built, food, social, and organizational environment influences. With health and policy implications, the results indicate that the schools’ walkability, food access, and extent of neighboring open campus policy-schools are significantly associated with open campus policy holding in Oregon.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Core Discussion Networks of Americans
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Determinants of fruit and vegetable consumption among children and adolescents: a review of the literature. Part I: quantitative studies
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found