- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prevalence of psychological symptoms among Ebola survivors and healthcare workers during the 2014-2015 Ebola outbreak in Sierra Leone: a cross-sectional study
Read this article at
Abstract
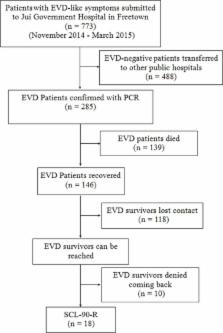
The 2014–2015 Ebola epidemic was considered to be the largest and most complex outbreak, which caused 11,310 reported deaths. The epidemic disease can cause a mental health crisis, however, there is only a small amount of scientific literature available related to this health issue so far. We evaluated the psychological symptoms of 161 participants including Ebola survivors and healthcare workers in Sierra Leone, analyzed the impact of job classification, education level on psychological status. We found that the order of total general severity index (GSI) scores from high to low was EVD survivors, SL medical staff, SL logistic staff, SL medical students, and Chinese medical staff. There were 5 dimensions (obsession-compulsion, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, and paranoid ideation) extremely high in EVD survivors. GSI were associated with university education negatively. We believed our information is necessary to develop the comprehensive emergency response plan for emerging infectious disease outbreak.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Sudan, 1976. Report of a WHO/International Study Team.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Symptom Check-List-90-R (SCL-90-R): a German validation study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found