- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nano/Microparticles and Their Combinations against Pathogenic Microorganisms for Biomedical Applications: From Physicochemical Characteristics to Pharmacological Aspects
Read this article at
Abstract
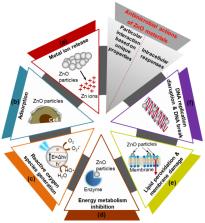
Zinc oxide (ZnO) nano/microparticles (NPs/MPs) have been studied as antibiotics to enhance antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria and viruses with or without antibiotic resistance. They have unique physicochemical characteristics that can affect biological and toxicological responses in microorganisms. Metal ion release, particle adsorption, and reactive oxygen species generation are the main mechanisms underlying their antimicrobial action. In this review, we describe the physicochemical characteristics of ZnO NPs/MPs related to biological and toxicological effects and discuss the recent findings of the antimicrobial activity of ZnO NPs/MPs and their combinations with other materials against pathogenic microorganisms. Current biomedical applications of ZnO NPs/MPs and combinations with other materials are also presented. This review will provide the better understanding of ZnO NPs/MPs as antibiotic alternatives and aid in further development of antibiotic agents for industrial and clinical applications.
Related collections
Most cited references155
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Curcumin: A Review of Its’ Effects on Human Health
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found