- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Association of Arch Stiffness with Plantar Impulse Distribution during Walking, Running, and Gait Termination
Read this article at
Abstract
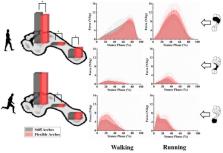
The purpose of this study was to determine relationships between arch stiffness and relative regional impulse during walking, running, and stopping. A total of 61 asymptomatic male subjects volunteered to participate in the study. All were classified by calculating the arch stiffness index using 3-dimensional foot morphological scanning. Plantar pressure distribution data were collected from participants using a Footscan pressure platform during gait tests that included walking, running, and gait termination. The stiff arches group ( n = 19) and flexible arches group ( n = 17) were included in the following data analysis. The results suggested that subjects with stiffer arches had a larger and smaller percentage of plantar impulse in the forefoot and rearfoot, respectively, than subjects with more flexible arches during walking and running. However, during gait termination, which included planned and unplanned gait stopping, the plantar impulse distribution pattern was found to be reversed. The current findings demonstrate that the distributional changes of plantar loading follow unidirectional transfer between the forefoot and the rearfoot on the plantar longitudinal axis. Moreover, the patterns of impulse distribution are also different based on different gait task mechanisms.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The foot core system: a new paradigm for understanding intrinsic foot muscle function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intrinsic foot muscles have the capacity to control deformation of the longitudinal arch.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found