- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparative investigation of reusable and single–use flexible endoscopes for urological interventions
Read this article at
Abstract
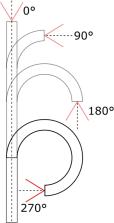
In order to evaluate the technical adaptability of a type of disposable endoscope compared to reusable flexible endoscopes, in vitro and in vivo studies were conducted. A disposable digital ureteroscope (“chip on tip”) and two reusable endoscopes were investigated with respect to spatial resolution, geometric distortion in air and water the maximum. Additionally, the clinical performance of the disposable device was tested during clinical procedures (n = 20). The disposable endoscope showed an optical resolution of 6.72 lines/mm at 10 mm distance, similar to the other devices. In comparison, the disposable endoscope showed a barrel-shaped image distortion in air of −24.2%, which is in the middle range, but was best under water (−8.6%). The bendability of 297° (275 µm fiber) and 316° (empty channel, 1.5 F basket) and the maximum irrigation (1 m: 58.1 ml/min, 2 m: 91.9 ml/min) were convincing. Clinically the maneuverability was very good in (13/20), good or satisfactory in (7/20). Visibility was evaluated as very good in (11/20), just in (1/20) either satisfactory or sufficient. The consistency of visibility was not affected in (19/20). In all cases there were no adverse events. The technical examination and clinical application of the disposable endoscope are of equal quality compared to reusable devices. Disposable endoscopes can be an alternative to reusable devices, but economic aspects such as reduction of repair costs, sterilization effort and additional waste must be taken into account.
Related collections
Most cited references24

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
2007 guideline for the management of ureteral calculi.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found