- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Graphene and water-based elastomers thin-film composites by dip-moulding
Read this article at
Abstract
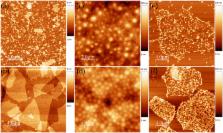
Thin-film elastomers (elastic polymers) have a number of technologically significant applications ranging from sportswear to medical devices. In this work, we demonstrate that graphene can be used to reinforce 20 micron thin elastomer films, resulting in over 50% increase in elastic modulus at a very low loading of 0.1 wt%, while also increasing the elongation to failure. This loading is below the percolation threshold for electrical conductivity. We demonstrate composites with both graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide, the reduction being undertaken in-situ or ex-situ using a biocompatible reducing agent in ascorbic acid. The ultrathin films were cast by dip moulding. The transparency of the elastomer films allows us to use optical microscopy image and confirm the uniform distribution as well as the conformation of the graphene flakes within the composite.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The real graphene oxide revealed: stripping the oxidative debris from the graphene-like sheets.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Evolution from graphite to graphene elastomer composites
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Book Chapter: not found