- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Reference-free cell mixture adjustments in analysis of DNA methylation data
Read this article at
Abstract
Motivation: Recently there has been increasing interest in the effects of cell mixture on the measurement of DNA methylation, specifically the extent to which small perturbations in cell mixture proportions can register as changes in DNA methylation. A recently published set of statistical methods exploits this association to infer changes in cell mixture proportions, and these methods are presently being applied to adjust for cell mixture effect in the context of epigenome-wide association studies. However, these adjustments require the existence of reference datasets, which may be laborious or expensive to collect. For some tissues such as placenta, saliva, adipose or tumor tissue, the relevant underlying cell types may not be known.
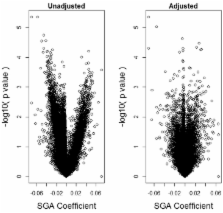
Results: We propose a method for conducting epigenome-wide association studies analysis when a reference dataset is unavailable, including a bootstrap method for estimating standard errors. We demonstrate via simulation study and several real data analyses that our proposed method can perform as well as or better than methods that make explicit use of reference datasets. In particular, it may adjust for detailed cell type differences that may be unavailable even in existing reference datasets.
Availability and implementation: Software is available in the R package RefFreeEWAS. Data for three of four examples were obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), accession numbers GSE37008, GSE42861 and GSE30601, while reference data were obtained from GEO accession number GSE39981.
Contact: andres.houseman@ 123456oregonstate.edu
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Related collections
Most cited references14
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Strong control, conservative point estimation and simultaneous conservative consistency of false discovery rates: a unified approach
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Analysing and interpreting DNA methylation data.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found