- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Psychological distress among Italians during the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) quarantine
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Quarantine as a preventive action to reduce people’s exposure to a contagious disease has substantial psychological impact. We aimed to collect information on psychologically distressing experiences of Italians living in quarantine during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
From 6 to 20 April 2020 participants filled out an online questionnaire. Demographic and physical symptoms data from the prior 14 days of quarantine were collected. Psychological impact of quarantine was assessed by the COVID-19 Peritraumatic Distress Index (CPDI).
Results
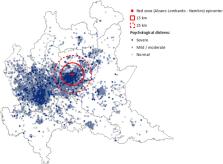
In all, 20,158 participants completed the online survey. Of these, 11,910 (59.1%) were from Lombardy, the region with 37.7% of positive cases identified during the survey period. 30.1% of responders were male. About half (55.9%) of responders were 18–50 years old, 54.3% had a tertiary level of education, 69.5% were workers, 84.1% were living in houses with ≥3 rooms, and 13.7% were living alone. 9.7% had had contact with COVID-19 positive people. Of all responders, 9978 (48.6%) reported a psychological impact, 8897 (43.4%) of whom reported mild or moderate and 1081 (5.2%) severe psychological impact. The multivariate analysis, after adjustments, showed that an increasing CPDI score was associated with gender (female), first-second educational level, being unemployed, living in a ≤2 room house, having had new health problems during the previous 14 days, and not having been out of the house in the previous week. Concerning the type of psychological distress, 2003 responders (9.9%) reported moderate to severe depressive symptoms, 1131 (5.5%) moderate to severe anxiety symptoms, and 802 (3.9%) moderate to severe physical symptoms. A positive correlation was found between responder rate (per 10.000 residents) and positive COVID-19 cases (per 10.000 residents) by region (r s = + 0.83, p = < 0.0001), and between responder rate and region latitude (r s = + 0.91, p = < 0.0001), with a greater response rate in the north. Considering Lombardy Region responders, a negative correlation between CPDI score and distance from place of residence to the red zone (Nembro-Alzano) was found. Higher prevalence of psychological distress was found up to 25 km away from the red zone and, in particular, severe distress up to 15 km.
Conclusions
Policy makers and mental health professionals should be aware of quarantine’s adverse mental health consequences. Factors influencing the success of quarantine and infection control practices for both disease containment and community recovery should be identified and additional support to vulnerable persons at increased risk of adverse psychological and social consequences of quarantine should be guaranteed.
Related collections
Most cited references54
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Immediate Psychological Responses and Associated Factors during the Initial Stage of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Epidemic among the General Population in China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found