- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Toward dynamic urban environmental exposure assessments in mental health research
Read this article at
Abstract
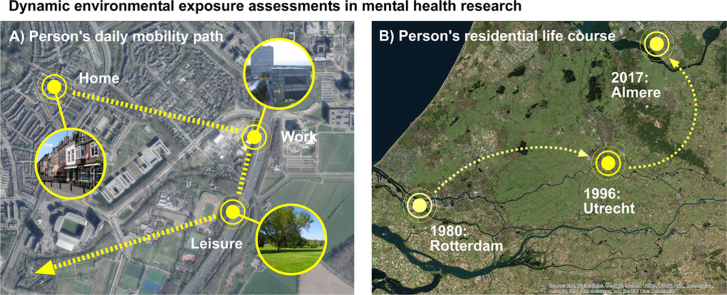
It is increasingly recognized that mental disorders are affected by both personal characteristics and environmental exposures. The built, natural, and social environments can either contribute to or buffer against metal disorders. Environmental exposure assessments related to mental health typically rely on neighborhoods within which people currently live. In this article, I call into question such neighborhood-based exposure assessments at one point in time, because human life unfolds over space and across time. To circumvent inappropriate exposure assessments and to better grasp the etiologies of mental disease, I argue that people are exposed to multiple health-supporting and harmful exposures not only during their daily lives, but also over the course of their lives. This article aims to lay a theoretical foundation elucidating the impact of dynamic environmental exposures on mental health outcomes. I examine, first, the possibilities and challenges for mental health research to integrate people's environmental exposures along their daily paths and, second, how exposures over people's residential history might affect mental health later in life. To push the borders of scientific inquiries, I stress that only such mobility-based approaches facilitate an exploration of exposure duration, exposure sequences, and exposure accumulation.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
The environmental context affects people's mental health.
-
•
Environmental exposure assessments are frequently restricted to the neighborhoods in which people currently live.
-
•
Dynamic exposures along people's daily paths may trigger mental disorders.
-
•
Exposures over people's residential history might affect mental health later in life.
-
•
Only dynamic exposure assessments enable the inclusion of the duration and sequence of exposures and risk accumulation over time.
Related collections
Most cited references83
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neighborhoods and health.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Uncertain Geographic Context Problem
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found