- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The nexus between forest fragmentation in Africa and Ebola virus disease outbreaks
Read this article at
Abstract
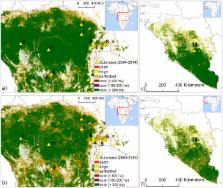
Tropical forests are undergoing land use change in many regions of the world, including the African continent. Human populations living close to forest margins fragmented and disturbed by deforestation may be particularly exposed to zoonotic infections because of the higher likelihood for humans to be in contact with disease reservoirs. Quantitative analysis of the nexus between deforestation and the emergence of Ebola virus disease (EVD), however, is still missing. Here we use land cover change data in conjunction with EVD outbreak records to investigate the association between recent (2004–2014) outbreaks in West and Central Africa, and patterns of land use change in the region. We show how in these EVD outbreaks the index cases in humans (i.e. spillover from wildlife reservoirs) occurred mostly in hotspots of forest fragmentation.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Analysis of Spatial Association by Use of Distance Statistics
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
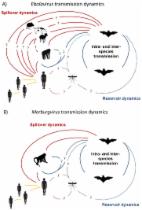
Filoviruses in Bats: Current Knowledge and Future Directions
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found