- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Habitat vulnerability in slum areas of India – What we learnt from COVID-19?
Read this article at
Abstract
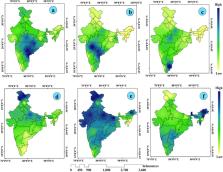
UN-Habitat identified the present COVID-19 pandemic as ‘city-centric’. In India, more than 50% of the total cases were documented in megacities and million-plus cities. The slums of cities are the most vulnerable due to its unhygienic environment and high population density that requires an urgent implementation of public healthcare measures. This study aims to examine habitat vulnerability in slum areas to COVID-19 in India using principal component analysis and Fuzzy AHP based technique to develop slum vulnerability index to COVID-19 (SVI covid-19). Four slum vulnerability groups (i.e. principal components) were retained with eigen-values greater than 1 based on Kaiser criterion - poor slum household status; lack of social distance maintenance; high concentrations of slum population and towns and mobility of the households. This study also mapped composite SVI covid-19 on the basis of PCA and Fuzzy AHP method at the state level for a better understanding of spatial variations. The result shows that slums located in the eastern and central parts of India (particularly Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal) were more vulnerable to COVID-19 transmission due to lack of availability as well as accessibility to the basic services and amenities to slum dwellers. Thus, the findings of the study may not only help to understand the habitat vulnerability in slum areas to COVID-19 but it will also teach a lesson to implement effective policies for enhancing the quality of slum households (HHs) and to reduce the health risk from any infectious disease in future.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The effect of human mobility and control measures on the COVID-19 epidemic in China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
