- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Field Sanitation and Foliar Application of Streptomyces padanus PMS-702 for the Control of Rice Sheath Blight
Read this article at
Abstract
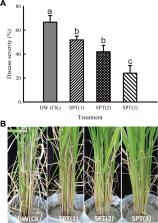
Rice sheath blight (ShB), caused by Rhizoctonia solani Kühn AG1-IA, is one of the destructive rice diseases worldwide. The aims of this study were to develop biocontrol strategies focusing on field sanitation and foliar application with a biocontrol agent for ShB management. Streptomyces padanus PMS-702 showed a great antagonistic activity against R. solani. Fungichromin produced by S. padanus PMS-702, at 3.07 mg/l inhibited 50% mycelial growth, caused leakage of cytoplasm, and inhibited the formation of infection structures of R. solani. Fungichromin could reach to 802 mg/l when S. padanus PMS-702 was cultured in MACC broth for 6 days. Addition of 0.5% S. padanus PMS-702 broth into soil decreased the survival rate of the pathogen compared to the control. Soil amended with 0.5% S. padanus broth and 0.5% tea seed pomace resulted in the death of R. solani mycelia in the infested rice straws, and the germination of sclerotia was inhibited 21 days after treatment. Greenhouse trials revealed that S. padanus cultured in soybean meal–glucose (SMGC-2) medium after mixing with different surfactants could enhance its efficacy for inhibiting the pathogen. Of six surfactants tested, the addition of 2% tea saponin was the most effective in suppressing the pathogen. S. padanus broth after being fermented in SMGC-2, mixed with 2% tea saponin, diluted 100 fold, and sprayed onto rice plants significantly reduced ShB disease severity. Thus, S. padanus PMS-702 is an effective biocontrol agent. The efficacy of S. padanus PMS-702 for disease control could be improved through formulation.
Related collections
Most cited references48

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Strategies for Fermentation Medium Optimization: An In-Depth Review
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found